What are the Data Spaces?
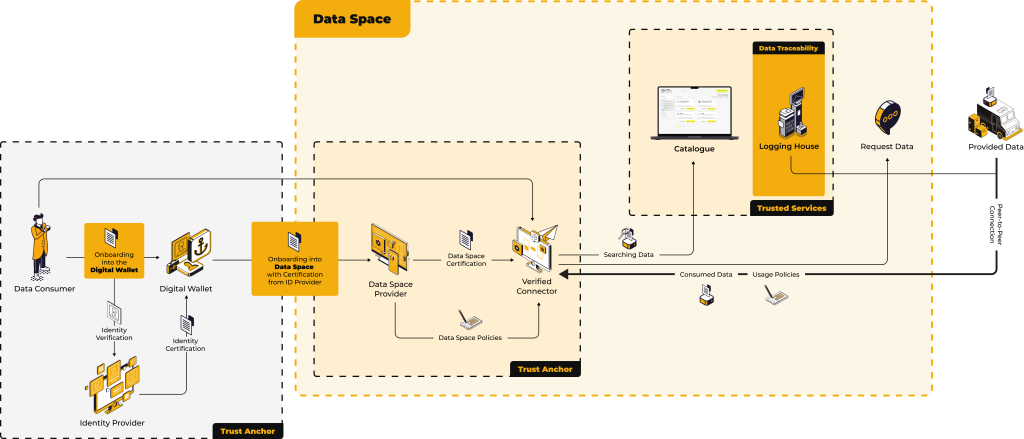
Data spaces are decentralized ecosystems designed to facilitate the trustworthy exchange of data. In a data space, different parties - data providers, consumers and intermediaries - interact within a framework that ensures security, privacy and compliance. This exchange usually takes place between digital wallets managed by identity providers and is supported by connectors that handle the secure transfer of data.
A data space allows individuals or organizations (data providers) to share their data with others (data consumers) while maintaining control over who accesses it and under what conditions. These environments are designed to respect data sovereignty, i.e. to ensure that data remains within a specific legal and regulatory framework, and to protect the privacy of users. Data Spaces promote trust, transparency and security, making it easier for organizations to share valuable information while reducing the risks associated with data breaches.
The onboarding process
Identity verification and digital wallets
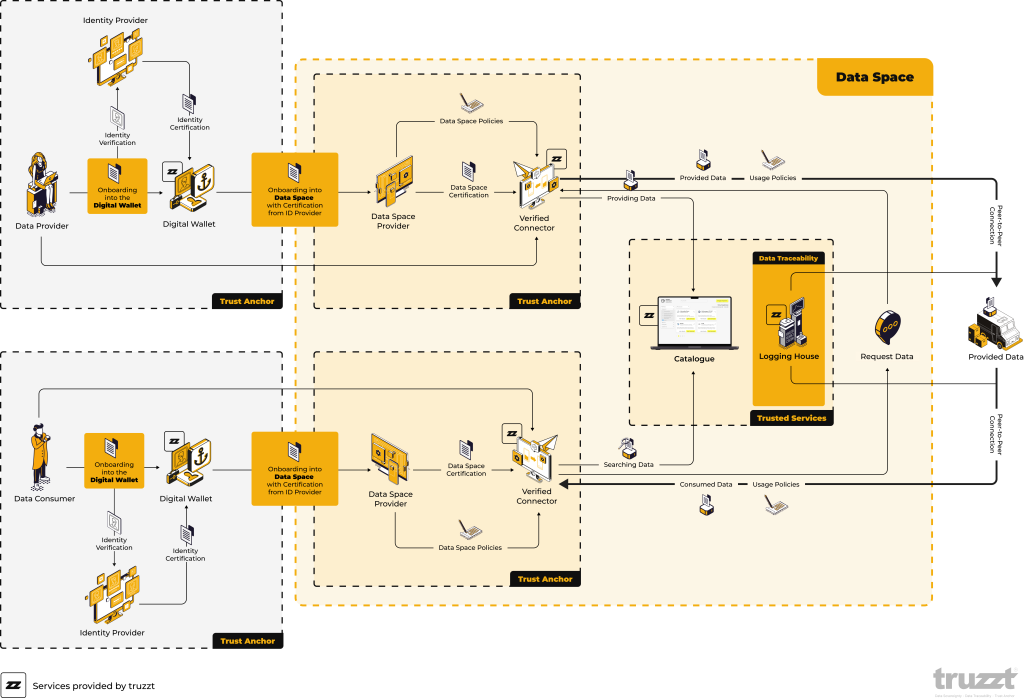
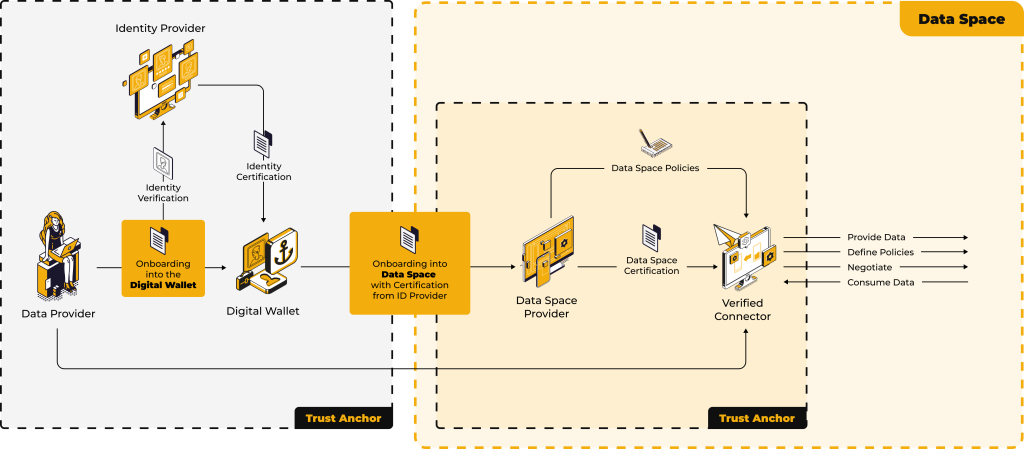
The onboarding process to a Data Space starts with identity verification. Users (either data providers or consumers) must submit their identity data to an identity provider. The identity provider verifies the user's credentials and issues a certificate that confirms the user's identity. This certificate is stored in a digital wallet, which serves as a secure storage space for the user's verified identity.
The connector is then used to access the data space. This software or tool is responsible for interacting with the data space, representing the user within the ecosystem and securely handling data exchange.
Who provides the digital wallet?
The digital wallet is provided and managed by trustworthy providers. These can be specialized companies or organizations that have experience in managing sensitive data. The wallet providers are responsible for the security of the stored credentials and ensure that only authorized persons can access them. In some cases, a wallet can also be integrated into the data space platform itself, which simplifies the process for users.
Data sharing and consumption
Data Provider
A data provider is a person or organization that makes valuable data available. By participating in a data room, data providers can upload and catalog their data and make it available to trusted data consumers. There are two reasons why data providers should participate in a data room:
Security
Data rooms ensure that the provider's data is only accessible to authorized users and protect it from unauthorized access or breaches.
Monetization
Providers can set terms of use that may include pricing for data usage, creating new revenue streams. A trusted environment such as a data room reduces friction when entering into agreements with consumers and ensures that all transactions are traceable and comply with data protection laws.
Data Consumer
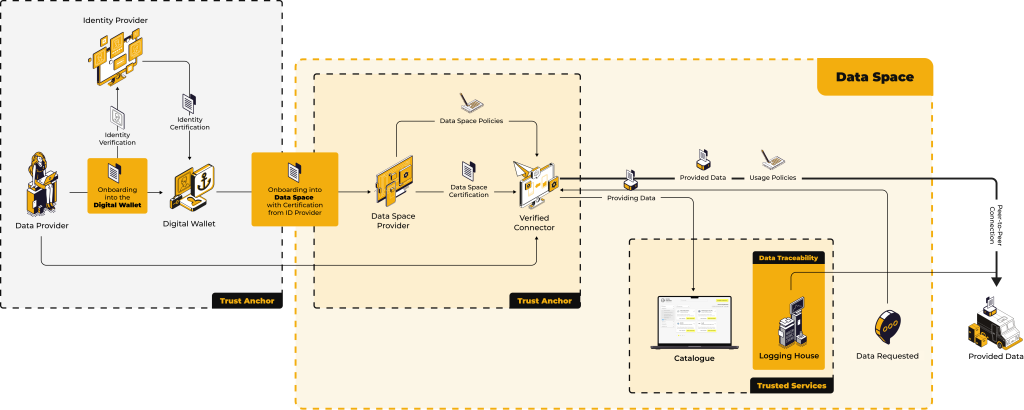
Data consumers, on the other hand, are looking for specific data that can improve their work. They can search for data and request it from providers in the field. The consumer's connector ensures that their request is properly vetted and complies with the provider's terms and conditions before the data is released.
Consumers benefit from the transparency of the data room as they can be sure that the data they receive is verified and trustworthy and comes from reputable providers.
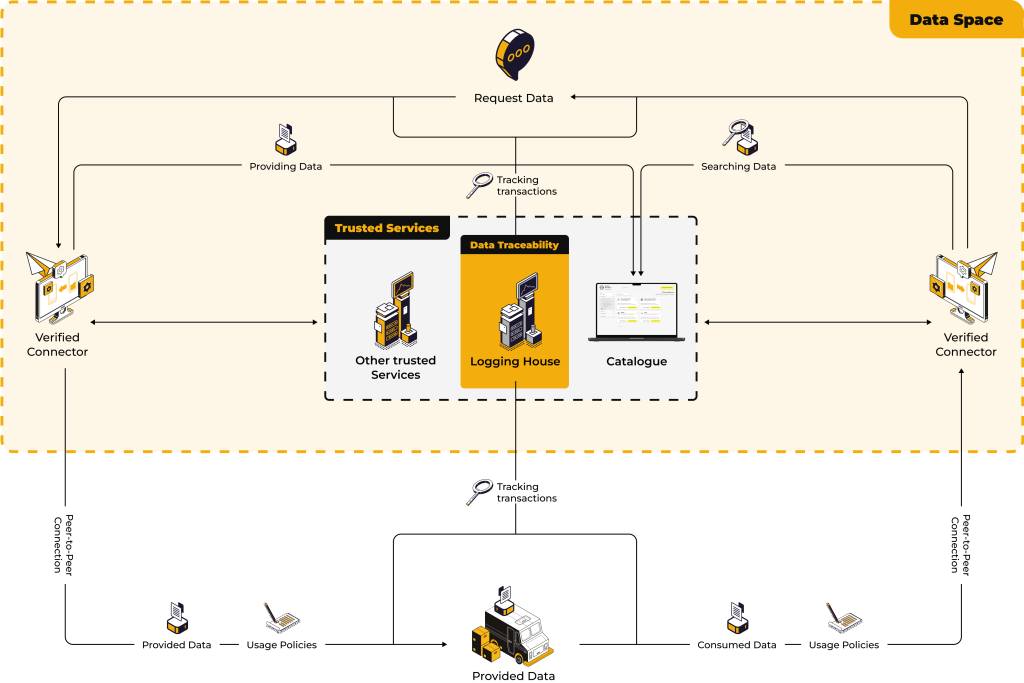
Ensuring trust and traceability
One of the most important components of a data room is the logging house. As data is exchanged between the two connectors, the logging house records each transaction to ensure traceability. This means that although the data itself is transferred directly between the connectors (outside the data room itself), the logging house maintains a secure audit trail.
Data Consumer
The transaction takes place directly between the two connectors, without a third party in the data room acting as an intermediary. This ensures that no unnecessary data is forwarded or stored and the risk of data leaks is minimized. The connectors act as trusted agents for both the data provider and consumer and handle the data exchange securely, while the logging point ensures that every action is tracked for future reference and compliance.